📝 Introduction
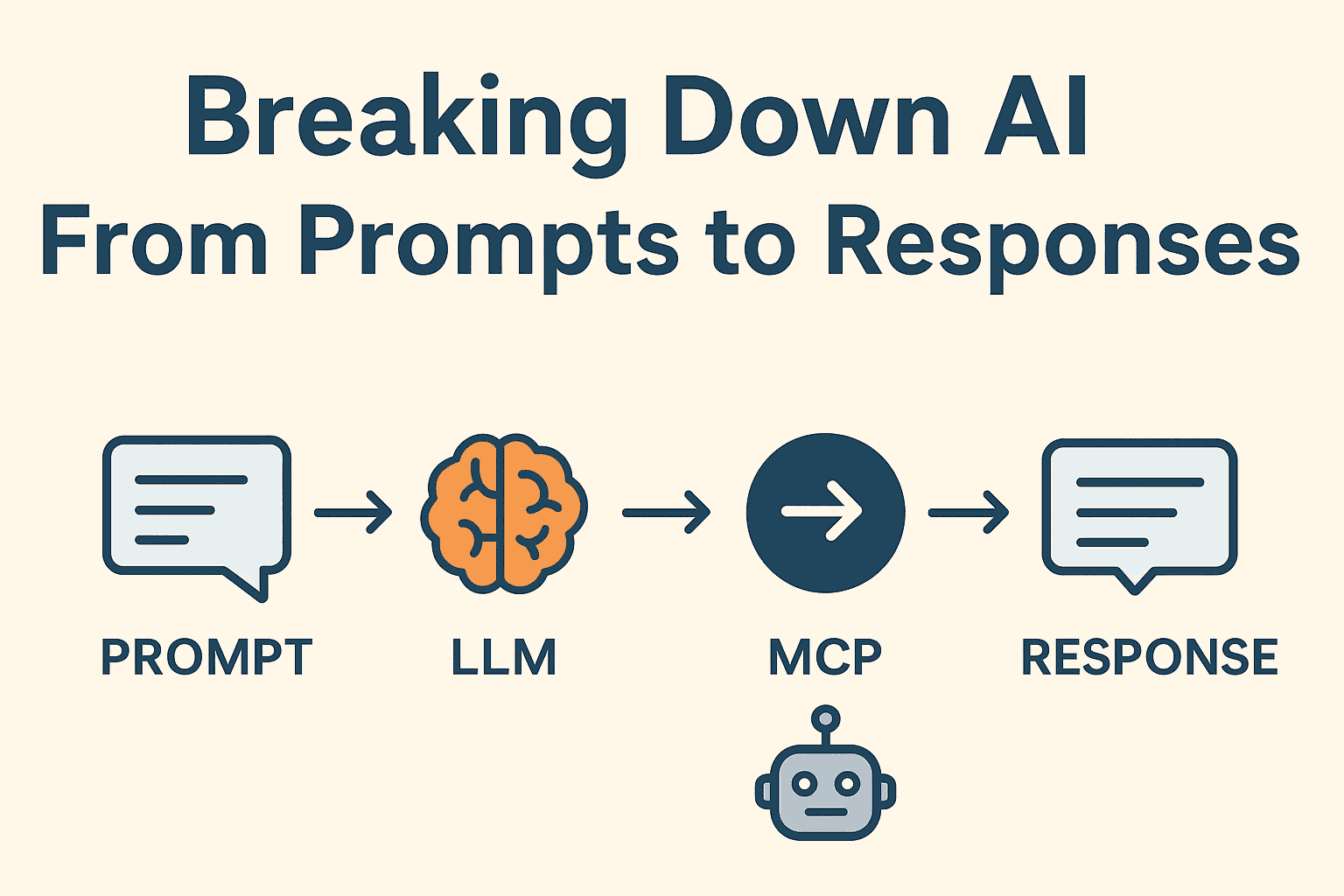
Artificial Intelligence can feel overwhelming with all the technical jargon—LLM, MCP, AI Agents, prompts, and more. But when broken down into simple terms, these concepts are much easier to understand. At its core, an LLM (Large Language Model) acts like the “brain,” the MCP (Model Context Protocol) serves as the messenger that bridges systems together, and the AI Agent is the assistant that carries out tasks. When you type a prompt into a web app, desktop app, or terminal, this entire system works together to understand your request, process it, and deliver a useful response back to you.
🔍 Breaking It Down: How It All Works
🧾 The Input Prompt – Your Question or Instruction
- This is what you say or type to the AI.
- Think of it like asking a question to a very smart person.
- Example: “What’s the weather tomorrow?” or “Write me an email.”
💻 Interface – How you send it
- You can give your prompt in different places, such as:
- Terminal User Interface (TUI) → Like talking to AI through a command-line window.
- Web User Interface (Web UI) → Like using ChatGPT in your browser.
- Desktop App Interface → Like having a standalone app on your computer.
🧠 LLM (Large Language Model) – The Brain
- An LLM (Large Language Model) is the “brain” of the AI.
- Just like a brain, it doesn’t directly do things in the real world—it mostly “thinks” and “talks.”
- It’s really good at understanding and generating human-like text (answers, advice, explanations, etc.).
- Think of it as the decision-maker that figures out what needs to be said or done.
🕹️ MCP (Model Context Protocol) – The Messenger / Translator
- The MCP is like the messenger or translator between the brain (LLM) and the outside world (apps, tools, systems).
- It makes sure the brain can understand what’s happening and pass along instructions.
- Example: If you ask the AI to check your calendar, the LLM doesn’t know how calendars work. The MCP helps connect the brain to your calendar app so the request makes sense.
🤖 AI Agent – The Assistant
- The AI Agent is the assistant or worker who takes the brain’s ideas and actually does things.
- It listens to the LLM (the brain), gets information via the MCP (the messenger), and then takes action.
- Example: If you tell the AI, “Book me a meeting for tomorrow at 10,” the agent is the one that goes into your calendar and schedules it.
🔄 The Flow: From Input to Output
Here’s how the cycle works:
- You give a prompt (your question or instruction).
- Interface passes it to the LLM (the brain).
- LLM processes it and, if needed, calls on MCP (the messenger).
- AI Agent performs the action (the assistant doing the task).
- Results go back through the LLM which translates them into clear, human-like responses.
- You see the output through the same interface you started with.
This is what makes interacting with AI feel natural—you ask, it thinks, something happens, and you get a response back. processes it, maybe performs actions, and then brings the response back to you through the same doorway you used.
❓ Q&A: Common Questions About AI (For General Audience)
Q1: Is the LLM the same thing as “AI”?
👉 Not exactly. The LLM is the brain of the AI, but an AI system can also include messengers (MCP), assistants (AI Agents), and interfaces where you interact. When people say “AI,” they often mean the whole system.
Q2: What’s a prompt?
👉 A prompt is simply your question or request to the AI. It can be typed into a chat box, a desktop app, or even a command-line terminal. The AI then processes your prompt and gives a response.
Q3: Can the AI do things on my computer by itself?
👉 Only if it’s connected to an AI Agent through something like MCP. The LLM alone can’t click buttons or move files—it just generates text and ideas.
Q4: Why does the AI sometimes make mistakes?
👉 Because the LLM doesn’t “know” things like a human. It works by predicting the best possible answer based on patterns it has learned. Sometimes that leads to errors, which is why it’s always good to double-check important results.
Q5: Do I need technical skills to use AI?
👉 Not at all! Most people use AI through simple interfaces like websites or apps. The technical parts (MCP, Agents, etc.) usually work behind the scenes, so you can just type in plain language and get results.
Q6: Will AI replace humans?
👉 AI is designed to assist people, not replace them entirely. It’s great for repetitive tasks, research, and drafting, but humans are still needed for creativity, judgment, and decision-making.
💡 Final Thoughts
Understanding the relationship between LLMs, MCP, AI Agents, and prompts helps demystify how modern AI tools really work. It’s not magic—it’s a structured flow where your input travels through interfaces, gets processed by the brain, is coordinated by the messenger, and executed by the assistant. As AI continues to evolve, knowing these basics will help everyday users and professionals alike appreciate how the technology operates behind the scenes.