Introduction
The world of IT security is changing at lightning speed. Remember when a strong firewall and a secure office perimeter felt like enough? Those days are largely behind us. With the rise of remote work, widespread cloud adoption, and increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, our traditional “castle-and-moat” security models are no longer sufficient. Once an attacker manages to breach that outer wall, they often have free rein inside, trusted implicitly simply because they’ve made it past the initial defenses.
This is where Zero Trust comes in. At its core, Zero Trust is a security principle built on one simple, powerful idea: “Never trust, always verify.” It’s not a product you can buy off the shelf; it’s a fundamental shift in how we approach security, assuming that nothing and no one, inside or outside our network, can be trusted by default. This approach dramatically reduces your attack surface, improves your ability to respond to incidents, and ultimately, better protects your valuable data. In this post, we’ll dive into what Zero Trust truly means, break down its core principles, show you how it works in practice, highlight its benefits, and offer practical steps to begin your Zero Trust journey.
What is Zero Trust, Really?
Zero Trust is a security model that moves away from the outdated assumption that everything inside an organization’s network is inherently safe. Instead, it operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” This means that every user, every device, and every application attempting to access your resources must be authenticated and authorized, regardless of whether they are within your corporate network or connecting remotely.
Think of it like airport security, but applied to every interaction within your IT environment. At an airport, everyone, whether they’re a pilot, flight attendant, or passenger, goes through security checks. There’s no inherent trust granted just because you’re “inside” the airport. Similarly, with Zero Trust, a user trying to access a file server needs to be verified, even if they’re sitting at their desk in the main office. A device connecting to an application also needs to prove its legitimacy and health.
This model fundamentally flips the script on traditional security by embracing the mindset of “assume breach.” You operate as if an attacker could already be present within your network. This doesn’t mean you’re paranoid; it means you’re prepared. By eliminating implicit trust, Zero Trust forces explicit verification for every single access request, making it far more difficult for malicious actors to move freely once they gain a foothold.
The Core Principles of Zero Trust
Zero Trust isn’t just a catchy phrase; it’s built upon several foundational principles that guide its implementation. Understanding these is key to grasping how it works:
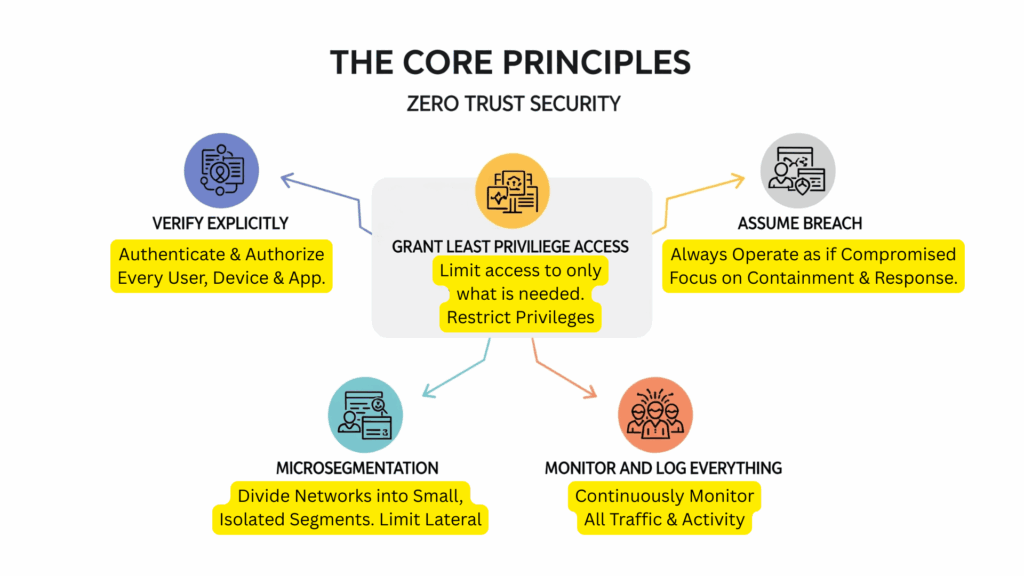
A. Verify Explicitly
This is the cornerstone of Zero Trust. It means that before granting any access, you must rigorously authenticate and authorize every user, device, and application. No exceptions. This goes beyond just a username and password. We’re talking about strong authentication methods like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), checking the health and compliance of the device being used, and verifying the user’s identity and role in real-time.
B. Grant Least Privilege Access
Once a user or device is verified, they should only be granted the absolute minimum access required to perform their specific task. This is often referred to as “least privilege.” If someone only needs to view a report, they shouldn’t have permissions to modify or delete it. This principle limits the potential damage if an account is compromised, as the attacker’s access will be severely restricted. Technologies like Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and just-in-time access play a huge role here.
C. Assume Breach
This isn’t about giving up; it’s about being realistic. The “assume breach” principle means designing your security posture with the understanding that, despite your best efforts, a breach is always a possibility. This shifts the focus from simply preventing breaches to rapidly detecting, containing, and responding to them. By assuming a breach, you build resilience into your systems, ensuring that even if an attacker gets in, they can’t easily move laterally or exfiltrate data.
D. Microsegmentation
Imagine your network isn’t one big open space, but a series of small, isolated rooms. That’s the idea behind microsegmentation. It involves dividing your network into tiny, distinct segments, each with its own specific security controls. If an attacker manages to compromise one segment, their ability to move to another part of your network (known as lateral movement) is drastically limited. This makes it far harder for them to reach critical assets or spread malware.
E. Monitor and Log Everything
To truly operate with Zero Trust, you need constant vigilance. This principle emphasizes continuous monitoring of all network traffic, user activities, and system behavior. Every access attempt, every data transfer, every system change – it should all be logged and analyzed. This comprehensive logging and monitoring are crucial for detecting anomalies, identifying suspicious activities, and enforcing security policies in real-time. If something looks out of place, you need to know about it immediately.
How Zero Trust Works in Practice
Let’s walk through a simple scenario to see how these principles come together in a Zero Trust environment. Imagine Sarah needs to access a sensitive sales report stored on a cloud-based server.
- Identity Verification: When Sarah tries to access the report, her identity isn’t just assumed. She’ll first go through a rigorous verification process, likely involving her username and password combined with a Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) prompt (e.g., a code from her phone or a biometric scan).
- Device Posture Check: Simultaneously, the system checks the “health” of Sarah’s laptop. Is it up-to-date with the latest security patches? Does it have an active antivirus? Is it free of suspicious software? If her device isn’t compliant, access could be denied or her access privileges limited until the issues are resolved.
- Policy Engine Evaluation: A central policy engine then takes all this information into account: Sarah’s verified identity, her role in the company (e.g., Sales Manager), the health of her device, the sensitivity of the sales report, and even contextual factors like her location and time of day.
- Least Privilege Access Granted: Based on the policy evaluation, Sarah is granted only access to that specific sales report. She doesn’t get blanket access to the entire sales server or other unrelated files. If the policy dictates she can only view, not edit, then that’s all she can do.
- Continuous Monitoring: Even after access is granted, Sarah’s activity is continuously monitored. If she suddenly tries to download the entire sales database, or access other files outside her normal scope, the system will flag this as suspicious behavior and could immediately revoke her access, alert security teams, or trigger further verification.
This entire process happens seamlessly and often transparently to the user, ensuring that every access decision is informed, verified, and strictly controlled.
Key Benefits of Adopting Zero Trust
Moving to a Zero Trust model isn’t just about buzzwords; it delivers tangible benefits that significantly bolster your organization’s security posture:
- Reduced Attack Surface: By requiring explicit verification for every access attempt, Zero Trust dramatically shrinks the potential entry points and pathways for attackers within your network.
- Improved Breach Containment: If a breach does occur (remember, we assume it can!), the microsegmentation and least privilege principles severely limit the attacker’s ability to move laterally and cause widespread damage. It’s like containing a fire to a single room instead of letting it burn down the whole house.
- Better Data Protection: With granular access controls and continuous monitoring, sensitive data is better protected from unauthorized access, whether from external attackers or malicious insiders.
- Enhanced Regulatory Compliance: Many regulatory frameworks (like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS) have strict requirements around data access and security. Zero Trust practices often help organizations meet these compliance obligations more effectively.
- Supports Remote Work & Cloud Adoption: Zero Trust is inherently designed for the modern workplace. It seamlessly secures access from anywhere, to anything, making it ideal for distributed workforces and hybrid cloud environments where traditional perimeters are obsolete.
- Simplified Security Management (Long-term): While initial implementation requires effort, the consistent policy enforcement and automated verification processes of Zero Trust can streamline ongoing security management and reduce manual oversight over time.
Getting Started with Zero Trust: A Pragmatic Approach for IT Pros
Adopting Zero Trust isn’t an overnight switch; it’s a strategic, iterative journey. You don’t have to overhaul your entire infrastructure at once. Here’s a pragmatic approach for IT professionals looking to begin:
- It’s a Journey, Not a Destination: Understand that implementing Zero Trust is a continuous improvement process. Start small, learn, and expand.
- Identify Your Crown Jewels: Begin by identifying your most critical assets, sensitive data, and high-value applications. These are your “crown jewels” – prioritize securing access to them first.
- Implement Strong Authentication (MFA Everywhere): This is foundational. If you’re not already using Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) across your organization, make it your top priority. It’s one of the easiest and most impactful ways to explicitly verify identities.
- Gain Visibility: You can’t secure what you can’t see. Invest in tools and practices that give you clear visibility into who is accessing what, from where, and with what device. Understand your current traffic flows and access patterns.
- Review and Refine Access Policies: Start challenging broad access permissions. Move away from “everyone can access X” to “only specific roles/users can access X, and only when necessary.” Implement least privilege wherever possible.
- Leverage Existing Tools: You likely already have many security tools that can contribute to a Zero Trust architecture. Your Identity and Access Management (IAM) solution, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools, Network Access Control (NAC), and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems are all key components. Focus on integrating and optimizing their use within a Zero Trust framework.
- Seek Knowledge: This is a complex area, so continue to learn. Attend webinars, read industry reports, and consider consulting with security specialists who have expertise in Zero Trust implementations.
Conclusion
The “Zero Trust” principle is more than just the latest cybersecurity buzzword; it’s a fundamental paradigm shift that’s essential for securing modern IT environments. By abandoning the outdated notion of implicit trust and embracing “never trust, always verify,” organizations can significantly enhance their defenses against an ever-evolving threat landscape. It’s about building resilience, limiting damage, and ensuring that every access decision is secure and justified.
While the journey to full Zero Trust implementation can be complex, starting with foundational steps like strong authentication and gaining better visibility into your network can set you on the right path. It’s time to stop thinking about a secure perimeter and start thinking about securing every single interaction, every single time.




