🚀 Curious about how your devices find their way to the internet?
In my latest blog post, I dive into the concept of the default route — often called the “gateway of last resort.” Whether you’re an IT professional, a DevOps enthusiast, or simply interested in networking, understanding how default routes work is essential for troubleshooting, optimizing, and securing your network.
🌐 Discover:
- What a default route is and why it matters
- How to check your default route on Windows, Linux, or Mac
- The role of default routes in network security and high availability
What is a Default Route?
A default route is a configuration in a network device that directs any packet with an unknown destination to a specified gateway or next-hop address. 🌐 It’s essentially a catch-all route used when no other specific route matches the destination IP address. In networking, the default route is often referred to as the “gateway of last resort.”
Concept of Default Route
The concept of a default route was introduced with the advent of IP networking and routing protocols. ⚡ Early network architects needed a mechanism to simplify routing tables, especially for connections to external networks like the Internet. Rather than maintaining detailed routes for every possible destination, the default route provides a streamlined solution.
The default route is represented as 0.0.0.0/0 in IPv4 and ::/0 in IPv6. 📂 This means that any IP address not explicitly defined in the routing table will follow the default route. Network administrators commonly configure default routes in routers, firewalls, and hosts to ensure seamless communication with external networks.
Why IT Professionals Need to Know
IT professionals, particularly those in network administration, DevOps, and cybersecurity, must understand default routes for the following reasons:
- 🔧 Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues: Identifying default route misconfigurations can resolve network outages.
- 🌐 Network Design and Optimization: Proper use of default routes simplifies routing table management. Ensuring efficient routing in complex environments.
- 🔒 Security Management: Default routes play a critical role in perimeter security. Preventing misconfigurations that could lead to network exposure.
- 🛡️ Multi-Homing and Failover: Managing redundant connections using multiple default routes ensures network resilience.
Does Every Device Connected to the Internet Have a Default Route?
Yes, most devices connected to the internet have a default route. 📱 Home routers, smartphones, computers, and even IoT devices typically have a default gateway configured to forward packets to the internet. Without a default route, devices would be unable to communicate beyond their local network.
Why is There Only One Default Route?
A device generally has only one default route because the concept is designed to simplify routing decisions. 🔄 However, in scenarios involving redundant internet connections or dual ISPs, network administrators may configure multiple default routes using technologies like BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) or load balancers to ensure failover and load distribution.
Routers use a concept called the Longest Prefix Match (LPM) to select the most specific route. When no match is found, the default route is applied. Maintaining a single default route avoids routing loops and ensures predictable behavior.
What Is a Gateway IP or Next Hop IP Address?
A gateway IP (or next hop) is the router’s IP address responsible for forwarding packets to their destination. It acts as an entry point for data leaving a local network.
Example:
- 🖥️ Device IP:
192.168.1.10 - 🌐 Gateway IP:
192.168.1.1 - 📡 All external traffic will be sent to
192.168.1.1.
How to Check Your Default Route
You can check your device’s default route using the following commands:
Windows OS 🖥️
route print and netstat -nr are the same output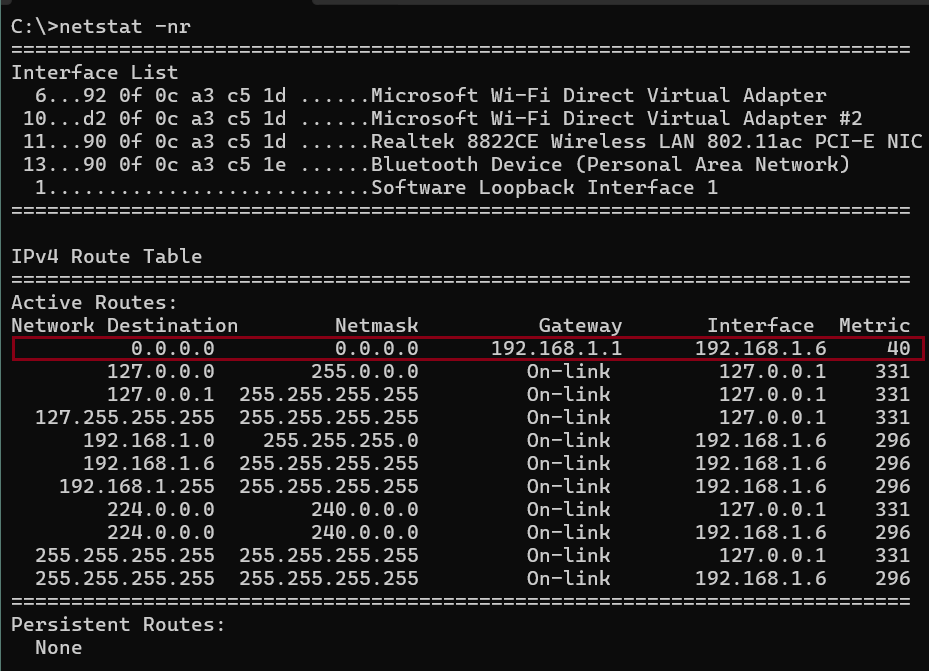
Linux OS 💻
netstat -nr
ip route show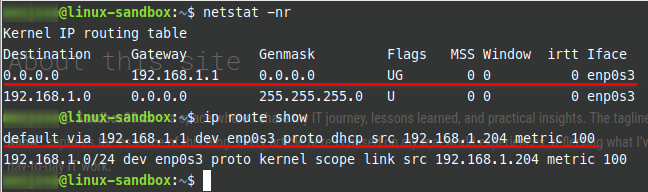
Mac OS 🤬
ip route show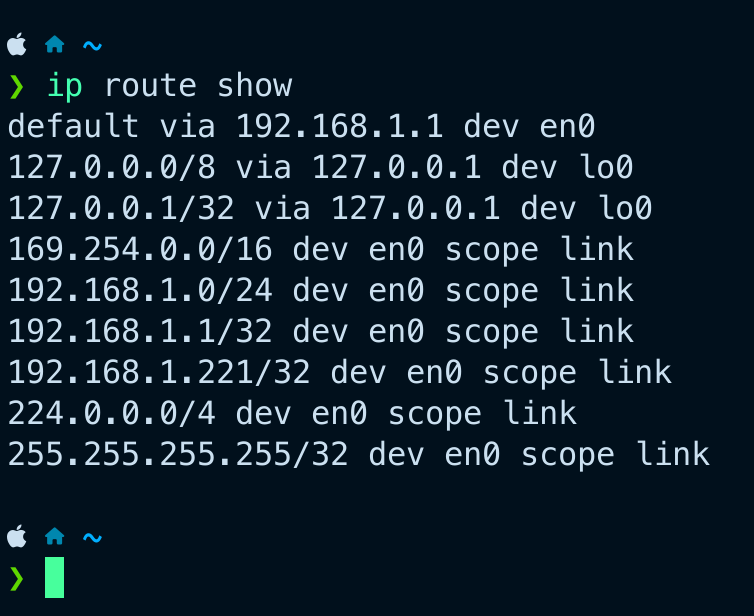
netstat -nr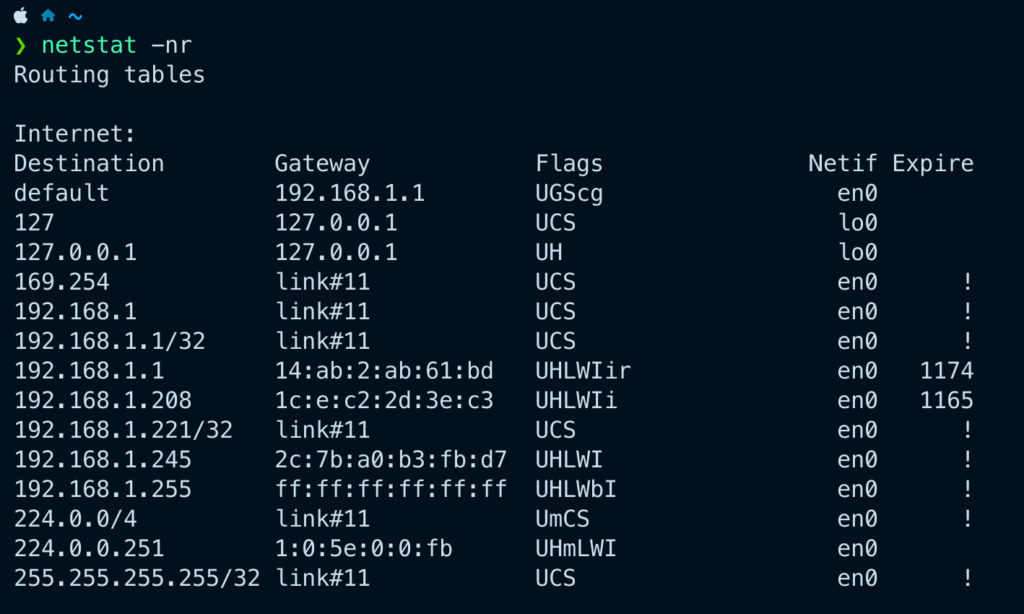
These commands display the default gateway and other routing information.
From a Security Perspective, Why Does It Matter?
The default route is a critical component of network security. 🔐 Misconfigured default routes can lead to data leaks, unauthorized access, or network outages. Threat actors often manipulate routing tables in attacks such as BGP hijacking. IT professionals must monitor default route configurations and apply firewall rules to mitigate these risks.
Best Practices:
- 🔧 Implement strict routing policies using firewalls and ACLs.
- 🛡️ Monitor routing tables for anomalies.
- 🔑 Use authenticated BGP sessions for external routing.
- ✅ Perform regular audits of default route configurations.
Redundancy and High Availability
For mission-critical applications, enterprises often use multiple ISPs with redundancy mechanisms like:
- 🔄 Floating Static Routes: Backup routes activated when the primary route fails.
- ⚙ ECMP (Equal-Cost Multi-Path): Balances traffic across multiple routes of equal cost.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the concept of the default route is essential for any IT professional dealing with networking. 🌐 Whether you are configuring routers, diagnosing connectivity issues, or ensuring network security, a solid grasp of default routing principles will serve you well. I didn’t include on how to modify or manipulate default route and don’t attempt to tweak if you don’t know what you’re doing. For now it’s fine that you read this blog and familiarize some new terminologies.
Further Reading
- 📖 RFC 1812 – Requirements for IP Version 4 Routers
- 🌟 Networking guides from Cisco, Juniper, or official documentation.
- 📚 Online courses on networking fundamentals like CCNA or CompTIA Network+.
- 📗 Cisco’s Guide to Static Routing
- 📙 Linux iproute2 Documentation
Stay curious, and keep learning!